Quantum communication is a technology that is transforming the way we share information. It provides unbreakable encryption and allows for instant transmission of data over any distance. This technology works by utilizing the entanglement of particles to ensure secure communication in fields such as finance, healthcare, and national security. Despite the technical challenges that still need to be addressed, the potential benefits for cybersecurity and privacy are immense. Therefore, responsible development and international cooperation are necessary to navigate this transformative technology and ensure a future of secure and interconnected communication.
Multi-Factor Magic: Manoeuvring Through the Maze of Multimodal Authentication
In the digital age, security is a paramount concern, leading to a shift from traditional password-based systems to multimodal authentication. This approach layers multiple defense mechanisms, including biometric identifiers like fingerprints, iris scans, voice recognition, and behavioral biometrics, along with knowledge-based factors such as passwords. By integrating these diverse methods, multimodal authentication offers a more robust defense against sophisticated cyber-attacks, enhancing the security and trustworthiness of digital transactions. The evolution from passwords to advanced biometrics marks a significant advancement in authentication methods, addressing the challenges of technological integration, privacy concerns, and balancing security with convenience. This new paradigm in security holds promise for a more secure, efficient, and user-friendly future in digital authentication.
Navigating Endpoint Security: Key Techniques and Practices
In today’s digital world, protecting your endpoints – be it desktops, laptops, or mobile devices – is crucial. These entry points can be exploited by attackers, causing breaches and devastating consequences. Endpoint security solutions act as your digital guardian, offering a shield against malware, phishing, ransomware, and more. By understanding detection techniques like signature-based, heuristic, and behavioural analysis, and implementing layered security with antivirus, IPS/IDS, and data encryption, you can safeguard your valuable data and ensure smooth operations. Investing in robust endpoint security is not just about technology, it’s about peace of mind.
Zero Trust Security: A New Standard for Cybersecurity
Zero Trust security is a proactive and robust safeguarding method that operates on four foundational principles: acknowledging the omnipresent possibility of a security breach, mandating verification for every transaction, limiting user and device access to the bare minimum required, and ensuring continuous monitoring both inside and outside the network. Unlike conventional security models, Zero Trust security operates at a more granular level, encapsulating each service with its security controls. The benefits of Zero Trust security include enhanced visibility into networks, facilitating compliance with industry regulations, and minimizing the impact of security incidents. However, the adoption of Zero Trust security comes with its share of challenges, such as a fundamental shift in organizational security approaches and substantial investments in new tools and specialized personnel.
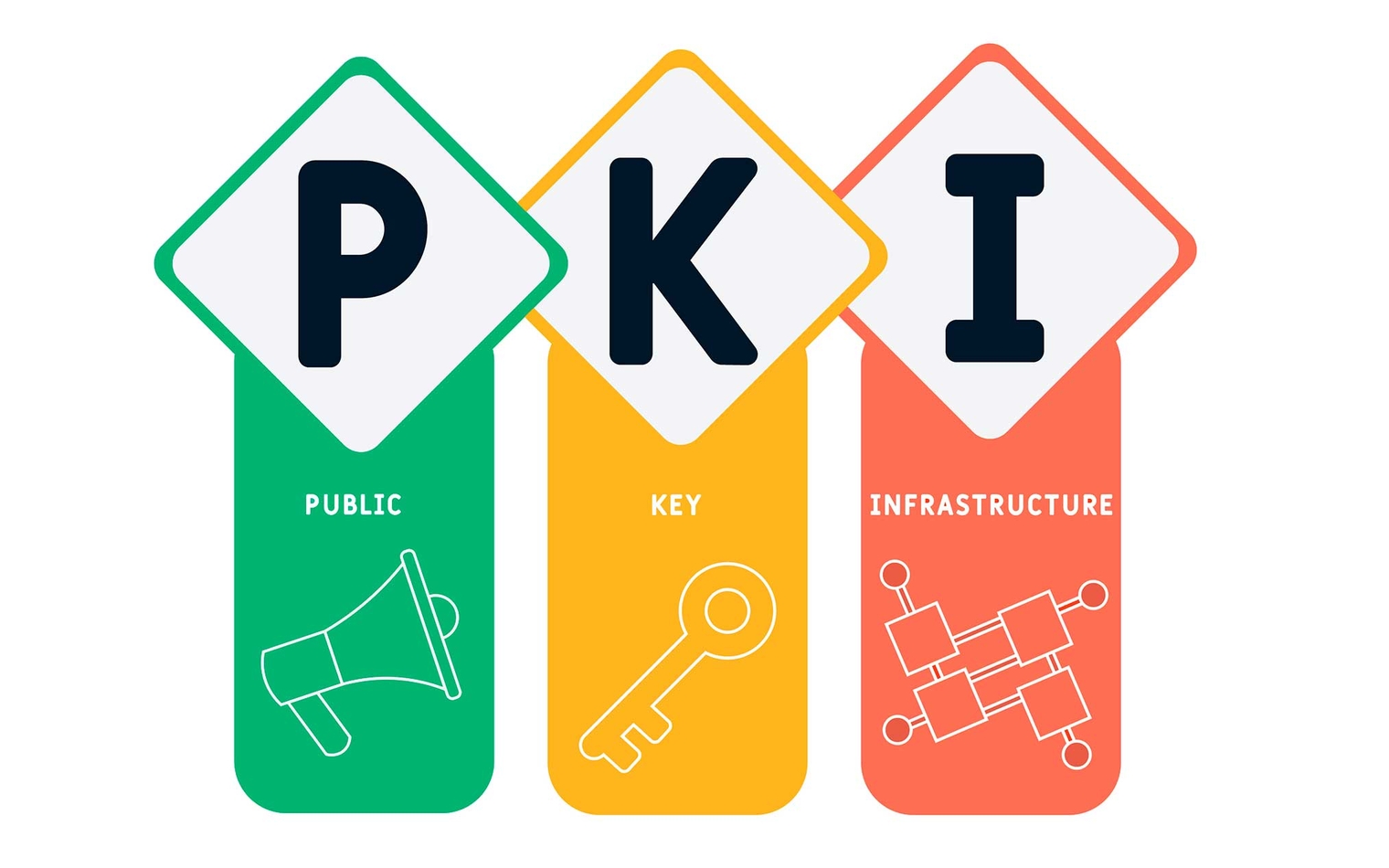
PKI’s Evolutionary Path: Redefining Security in the Digital Realm
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a comprehensive suite of technologies, policies, and procedures that ensure secure communication, confidentiality, integrity, and non-repudiation in the digital sphere. PKI operates through digital certificates issued by trusted Certification Authorities (CAs). PKI’s role is pivotal in fortifying online banking and financial transactions, global e-commerce, and secure data sharing in supply chains. PKI faces challenges such as managing keys and security threats. Innovations like Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) and Blockchain-based PKI solutions emerge as promising safeguards against these threats. PKI’s evolution extends to decentralized models and Identity-based cryptography, promising enhanced security and user-friendliness. PKI’s continued evolution ensures a resilient and trusted digital identity verification and encryption framework, facilitating secure, borderless digital interactions across industries and geographies.
Cybersecurity Essentials: Common Types of Cyberattacks and How To Prevent Them
Cyberattacks are a major threat to individuals and organizations, causing significant financial losses and damage. They can be initiated using a variety of techniques, including phishing, malware, and denial-of-service attacks. To protect oneself from cyberattacks, one can implement measures such as using strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, keeping software up-to-date, being cautious while opening emails or clicking on links, using anti-phishing software, and having an emergency plan in place. By following these guidelines, individuals can reduce their chances of falling victim to a cyberattack.
Data Security: Why Is It Important and How to Protect the Data
Data security is important to protect digital information from unauthorized access. Individuals and organizations can protect their data by using strong passwords, being careful about links and attachments, keeping software up to date, encrypting sensitive data, and backing up data regularly.
Cybersecurity – Staying Safe in the Digital Age
Digital security is a well-known word nowadays. Securing one’s digital identity is fundamental as the world is becoming increasingly digitalized. Digital identity represents the physical identity of someone within the […]
Tips for Staying Safe Online: Why Cybersecurity is Everyone’s Responsibility
What is the significance of cybersecurity? Because of the internet’s extensive effect on modern life, cybersecurity is essential. The potential for internet integration is limitless with the growing number of […]